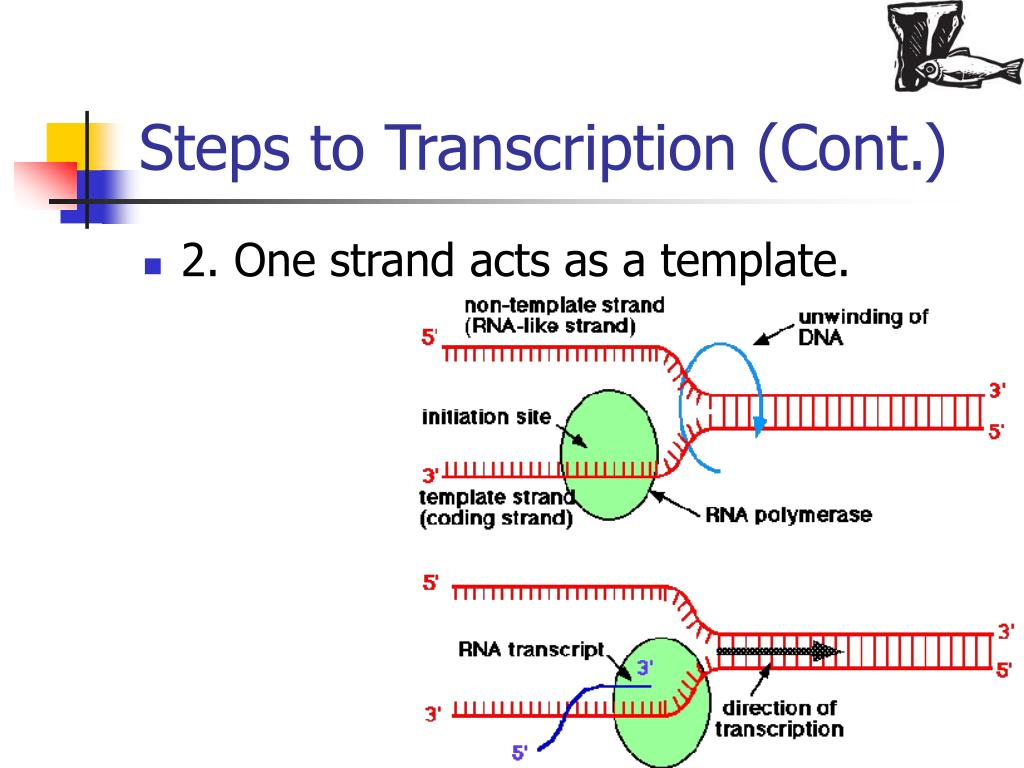
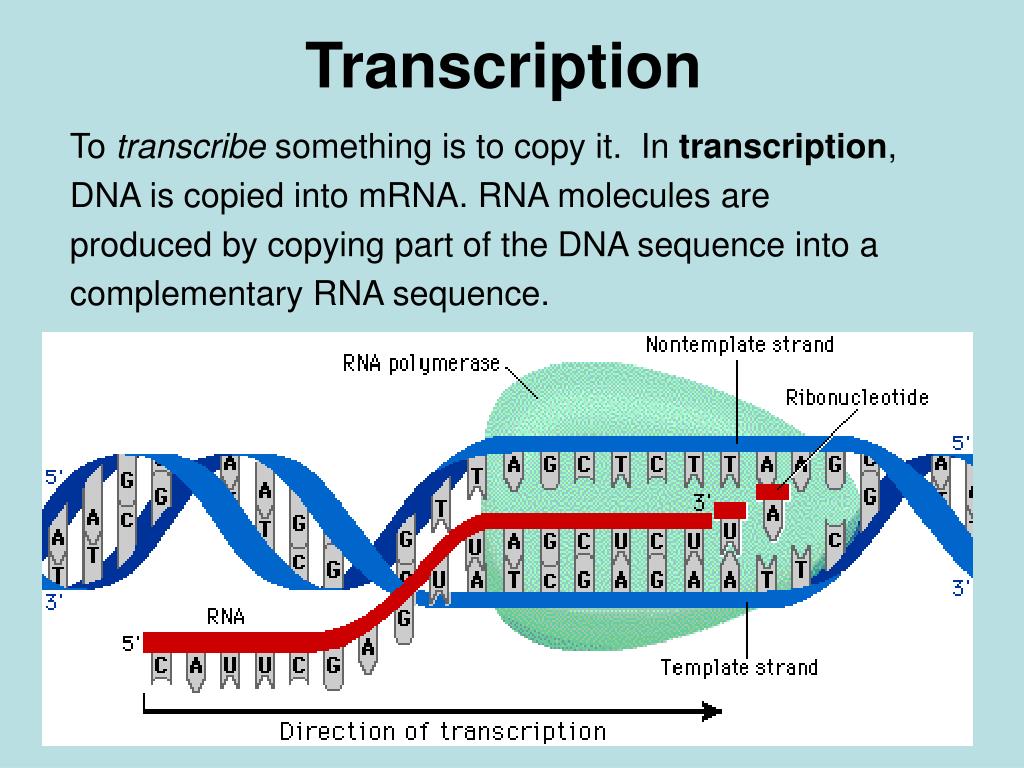
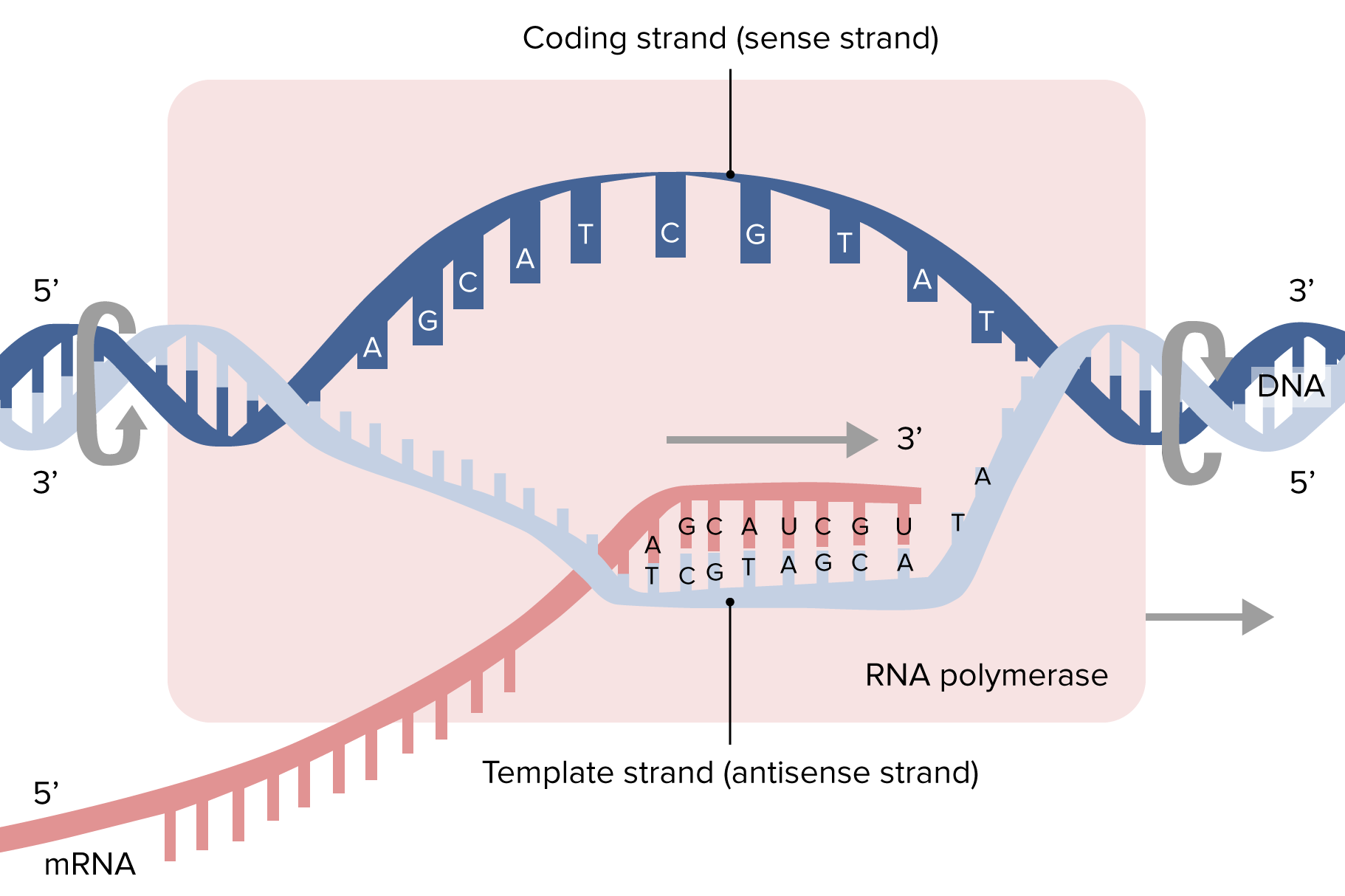
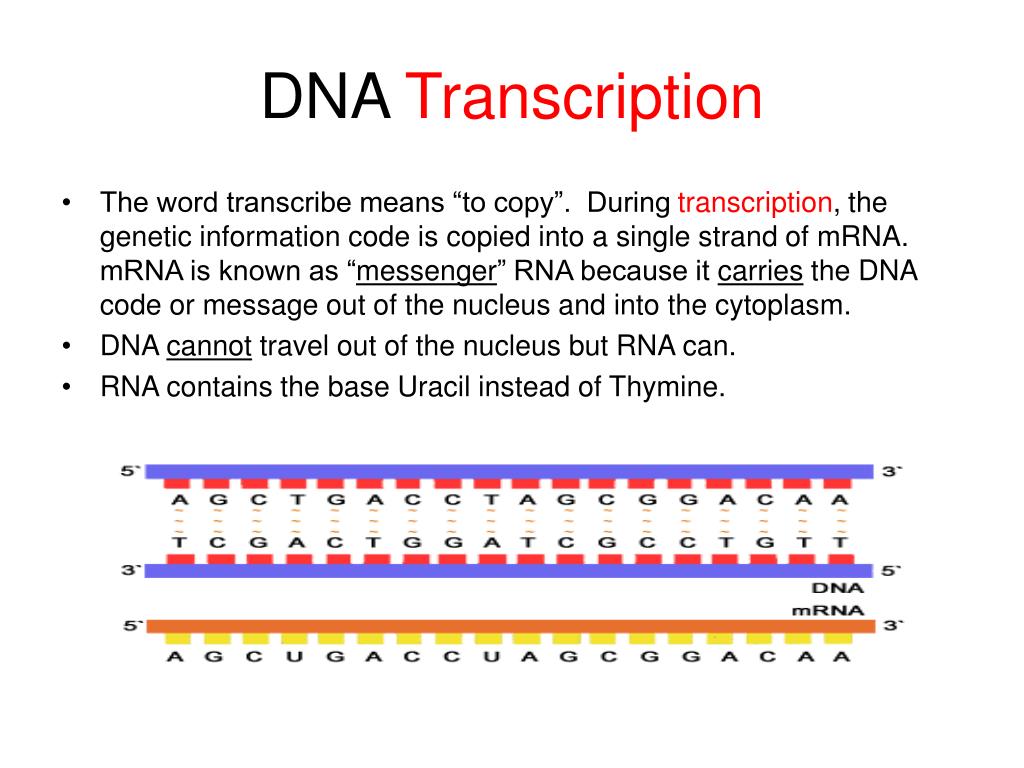
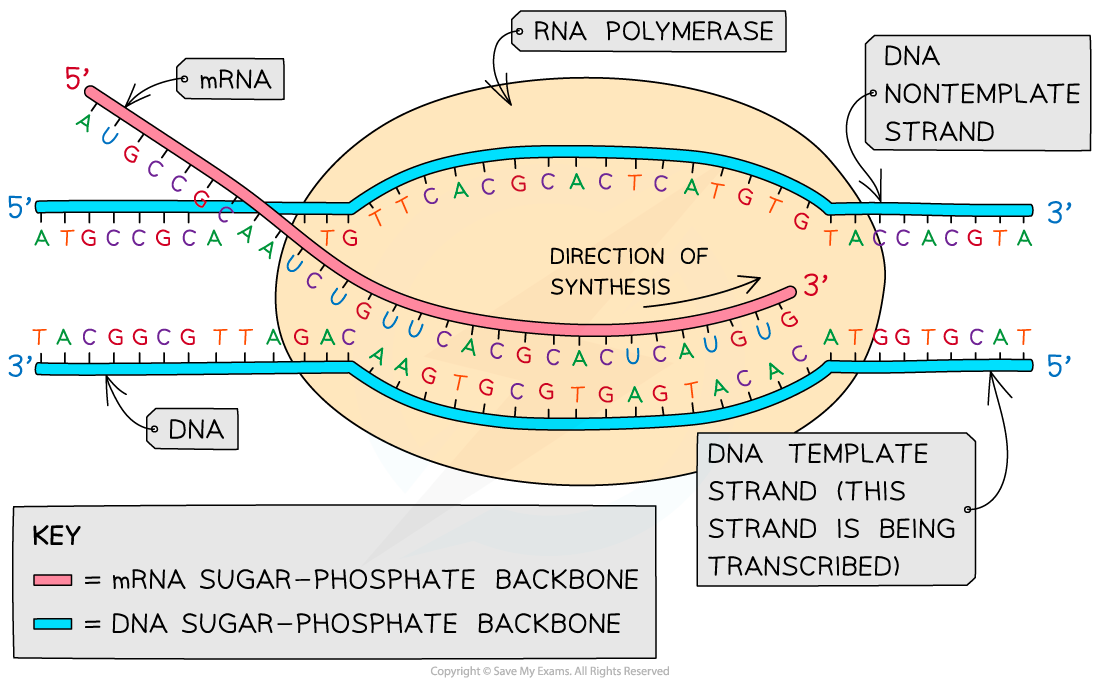
Web the basic steps of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The promoter is the binding site for rna polymerase. The nontemplate strand is referred. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna.
This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. Web the basic steps of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna.
The nontemplate strand is referred. Web the basic steps of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Here we can identify several of the dna sequences that characterize a gene. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.
This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The nontemplate strand is referred. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. It usually lies 5’ to, or upstream of the transcription start site. The promoter is the binding site for rna polymerase. Here we can identify several of the dna sequences that characterize a gene. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web the basic steps of transcription are initiation, elongation, and termination. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template).
Here We Can Identify Several Of The Dna Sequences That Characterize A Gene.
The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. This strand is called the template strand. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.
The Mrna Product Is Complementary To The Template Strand And Is Almost Identical To The Other Dna Strand, Called The.
Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template;
The Promoter Is The Binding Site For Rna Polymerase.
Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The nontemplate strand is referred. It usually lies 5’ to, or upstream of the transcription start site. This template strand is called the noncoding strand.