So, you need to dilute your dna sample first up to 8 times and use. What is the optimal amount of dna template that should be used for pcr? Pcr is based on using the ability of dna polymerase to synthesize new strand of dna complementary to the offered template strand. Pcr involves the enzymatic amplification of nucleic acid templates, and can be divided into four major steps, listed below. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna.
The addition of modified nucleotides (dntps) called dideoxyribonucleotides (ddntps). In many cases, dna is isolated from cell cultures or from microorganisms and subsequently used as a pcr template. For pcr templates, it is important that the product is purified away from the pcr reactants, especially the primers, as these can cause high background in the sequencing reaction. This tutorial reviews calculations that can be used for determining the mass of gdna and plasmid templates that correspond to copy numbers of target nucleic acid sequences. Pcr is a highly sensitive technique and requires only one or two dna templates for successful amplification.
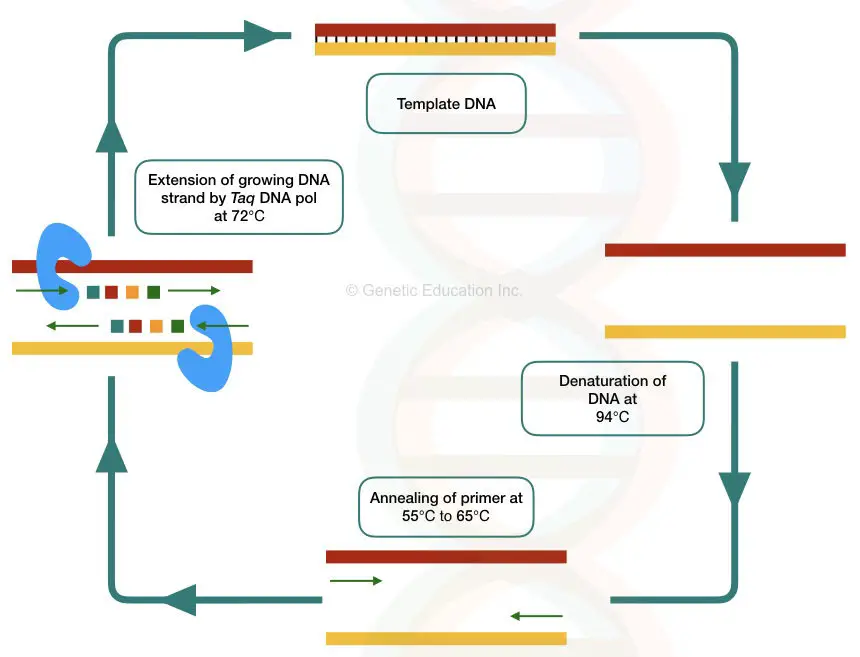
What are the critical factors for amplification of long genomic targets? Pcr primers are designed as pairs, referred to. Click editing uses dna polymerases, huh endonucleases and oligonucleotide templates for genome modification. The ingredients are assembled in a tube, along with cofactors needed by the enzyme, and are put through repeated cycles of heating and cooling that allow dna to be synthesized. The key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks).
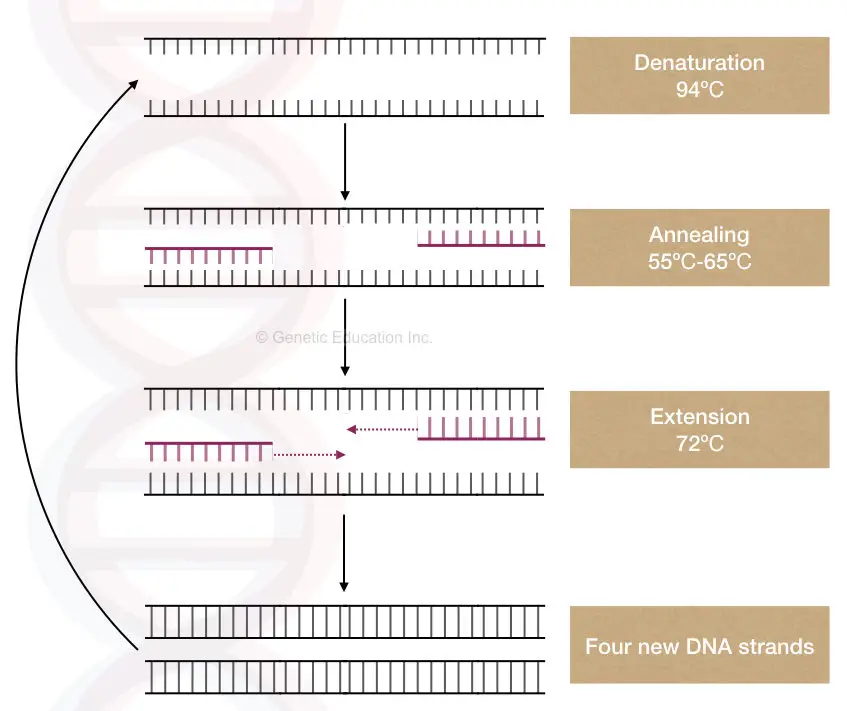
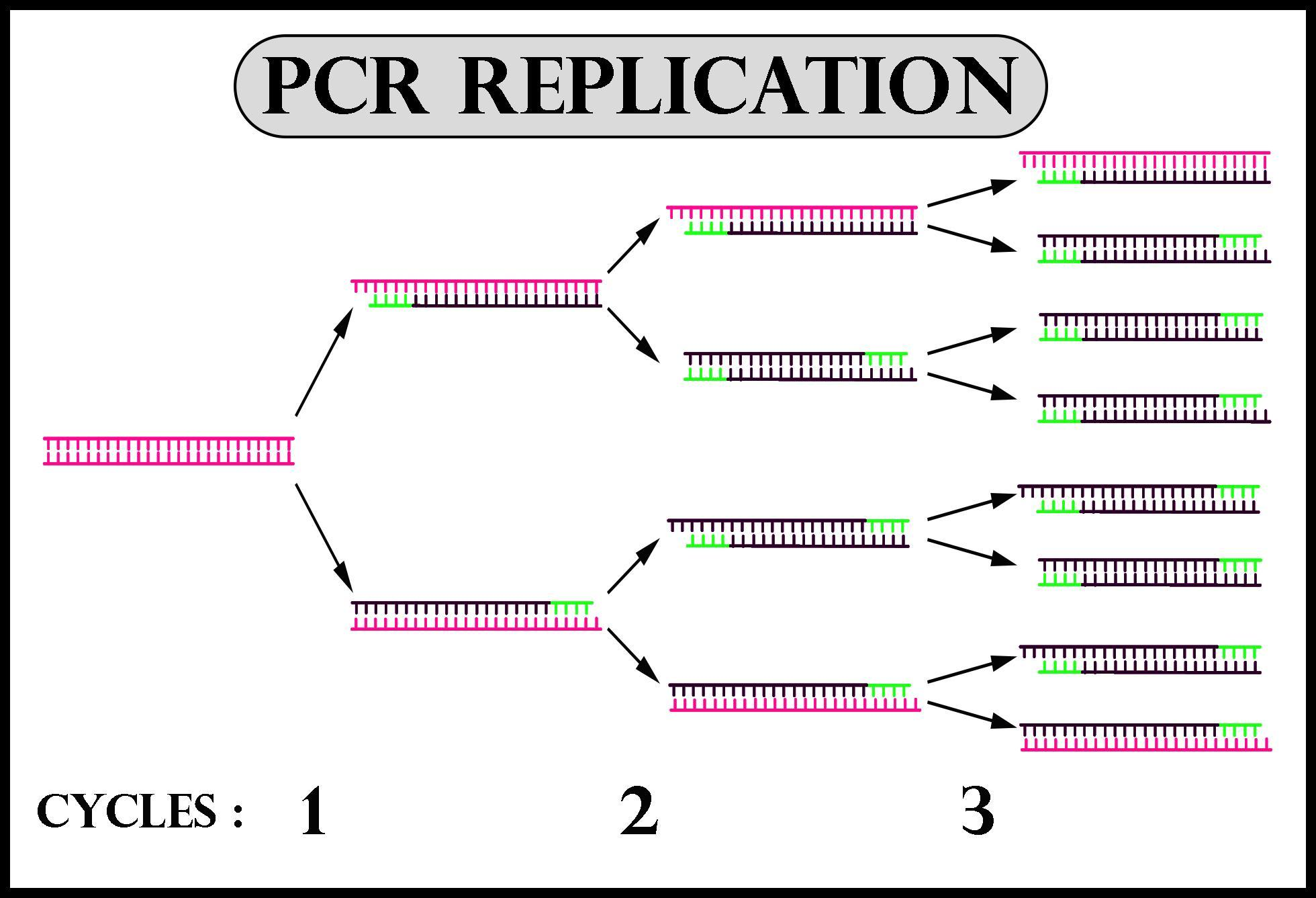
From a single copy of dna (the template), a researcher can create thousands of identical copies using a simple set of reagents and a basic heating and cooling. This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide treatment at 100°c for 10 min followed by centrifugation. Since the middle of the last century ( brown and watson, 1953 ), many protocols have been developed to extract dna from a variety of biological samples. Preparation of template dna is a critical step in pcr. Nevertheless, the composition or complexity of the dna contributes to optimal input amounts for pcr amplification. A standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq polymerase. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. Pcr involves the enzymatic amplification of nucleic acid templates, and can be divided into four major steps, listed below. The standard reaction conditions for pcr are: Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. For pcr templates, it is important that the product is purified away from the pcr reactants, especially the primers, as these can cause high background in the sequencing reaction. Short dna fragments bind complementary regions of the template to begin new strand synthesis. The key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks). To apply pcr to the study of rna, the rna sample must first be converted to cdna to provide the necessary dna template for the thermostable polymerase (figure 1). This tutorial reviews calculations that can be used for determining the mass of gdna and plasmid templates that correspond to copy numbers of target nucleic acid sequences.
The Amplification Is Achieved By Thermostable Taq Dna Polymerase Enzyme.
This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide treatment at 100°c for 10 min followed by centrifugation. Click editing uses dna polymerases, huh endonucleases and oligonucleotide templates for genome modification. The ph of the reaction buffer should be 8.3 when measured at 25c. Dna template in pcr amplification.
Short Dna Fragments Bind Complementary Regions Of The Template To Begin New Strand Synthesis.
Standard pcr reagents include a set of appropriate primers for the desired target gene or dna segment to be amplified, dna polymerase, a buffer for the specific dna polymerase, deoxynucleotides (dntps), dna template, and sterile water. Dna from a variety of sources may be used as the supplier of the dna template for 3 basic steps of the polymerase chain reaction. This tutorial reviews calculations that can be used for determining the mass of gdna and plasmid templates that correspond to copy numbers of target nucleic acid sequences. Preparation of template dna is a critical step in pcr.
Generally, No More Than 1 Ug Of Template Dna Should Be Used Per Pcr Reaction.
The standard reaction conditions for pcr are: The ingredients are assembled in a tube, along with cofactors needed by the enzyme, and are put through repeated cycles of heating and cooling that allow dna to be synthesized. The key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks). Pcr primers are designed as pairs, referred to.
To Apply Pcr To The Study Of Rna, The Rna Sample Must First Be Converted To Cdna To Provide The Necessary Dna Template For The Thermostable Polymerase (Figure 1).
Your dna template concentration is extremely high for pcr reaction. Pcr is based on using the ability of dna polymerase to synthesize new strand of dna complementary to the offered template strand. For pcr templates, it is important that the product is purified away from the pcr reactants, especially the primers, as these can cause high background in the sequencing reaction. Pcr involves the enzymatic amplification of nucleic acid templates, and can be divided into four major steps, listed below.